Difference between revisions of "RTU Master RTU Slave RTU Module"
(Created page with "<ul> <li> Master = com port paramters </li> <li> Slave = group modules </li> <li> Modules = Modbus ID (UnitID) and function code </li> </ul> <p>if you want to R/W to a...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | * Master = com port paramters | |
| − | + | * Slave = group modules | |
| − | + | * Modules = Modbus ID (UnitID) and function code | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if you want to R/W to a slave you need at least 2 modules per slave.<br /> | |
| − | + | The address in Module is used as address offset in the standard Modbus table.<br /> | |
| − | + | Use Uint16 for channel representation. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | For manual control of R/W, disable Continous and use SendOp flag.<br /> | |
| − | + | ||
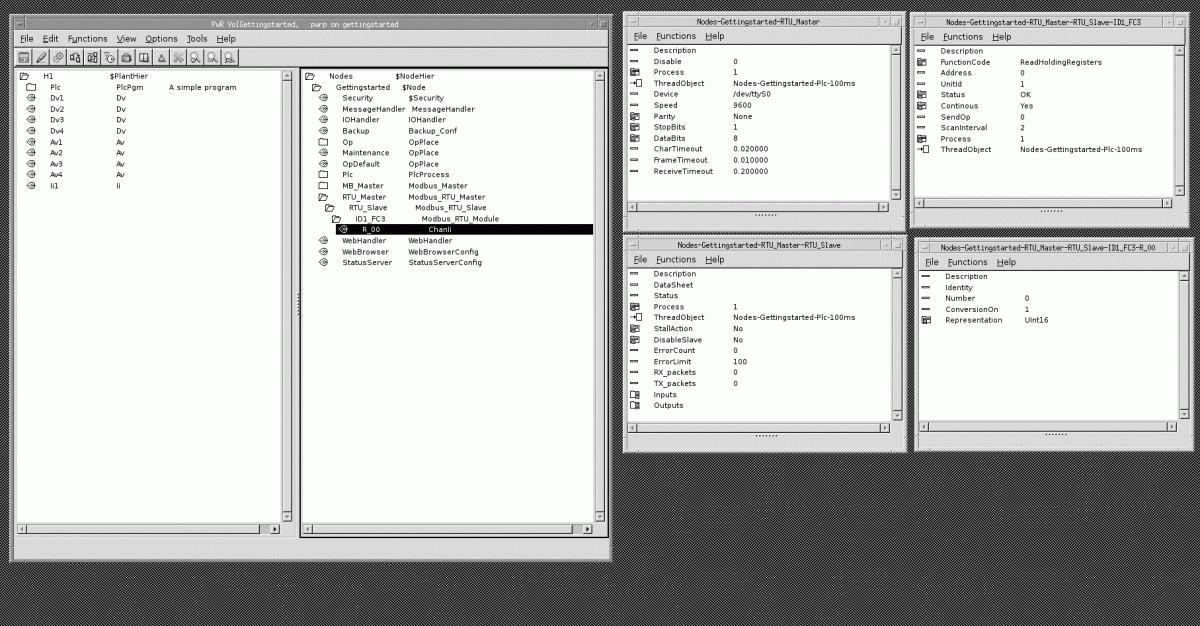
| + | If you let the PLC control de R/W (Process=1 and specify PLC thread), then in each scan cycle the PLC will use the module properties to send a commands to all modules it controls. <br /> | ||
| + | In the example case, the PLC will send one command to slave id = 1, command code = 03 (read holding registers), address = 0x0000 (default 40001).<br /> | ||
| + | For Continous=1 R/W is automatic.<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you need manual control of read/write cyle, which is somewhat disirable for slow connections, you need to set Continous=0, and use the SendOp flag from PLC or application. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:RTU M S M.gif]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:10, 22 August 2013
- Master = com port paramters
- Slave = group modules
- Modules = Modbus ID (UnitID) and function code
if you want to R/W to a slave you need at least 2 modules per slave.
The address in Module is used as address offset in the standard Modbus table.
Use Uint16 for channel representation.
For manual control of R/W, disable Continous and use SendOp flag.
If you let the PLC control de R/W (Process=1 and specify PLC thread), then in each scan cycle the PLC will use the module properties to send a commands to all modules it controls.
In the example case, the PLC will send one command to slave id = 1, command code = 03 (read holding registers), address = 0x0000 (default 40001).
For Continous=1 R/W is automatic.
If you need manual control of read/write cyle, which is somewhat disirable for slow connections, you need to set Continous=0, and use the SendOp flag from PLC or application.